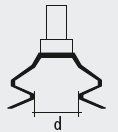
Vacuum Foam Gripper Calculation
vacuum foam gripper calculation is important for how to know about foam pad cell force and how many vacuum foam gripper to use in vacuum handling system.
Sample Theoretical Force Calculation
Vacuum level = -300 mbar
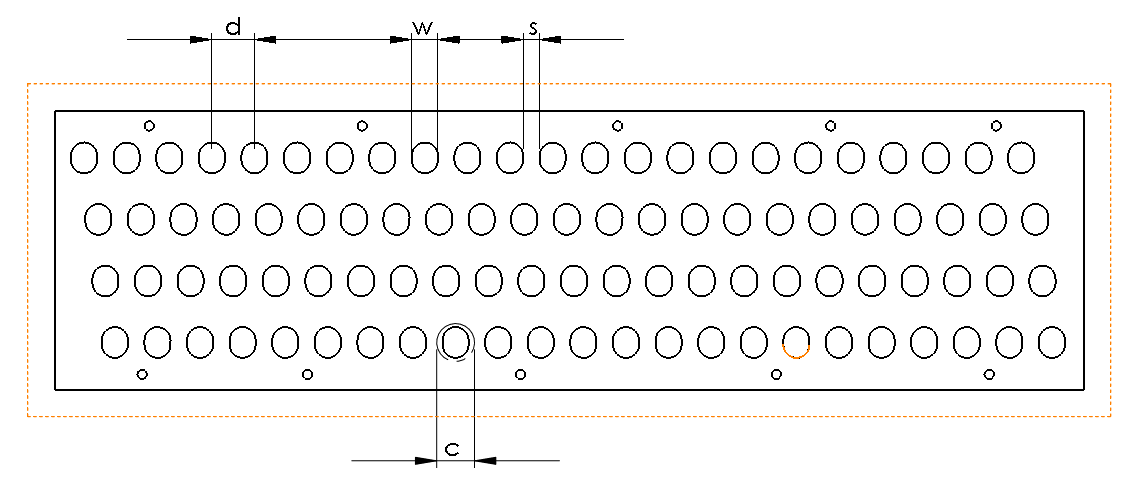
cell width = 11 mm
cell lenght = 13 mm
F = PA
= abs| – 300 / 100 | * 0.785 * ( 1.1 * 1.3 ) cm2
= 3.37 N/Cell
for online calculation click here...